Tech Council
Technology Articles
How to Plan Your AWS to Azure Migration in 2026
Learn how to migrate from AWS to Azure with proven strategies, cost estimates, and Microsoft tools. A complete guide for cloud transitions in 2026.

Denis Avramenko
CTO, Co-Founder, Streamlogic
Dec 11, 2025

Reading time: 8 minutes
Table of Contents
When does AWS to Azure migration make business sense?
What assessment steps are required before migration?
How much does AWS to Azure migration cost?
Which Azure tools simplify the migration process?
What migration strategy fits your workload?
How do you execute data transfer at scale?
What security measures protect your migration?
How can you minimize downtime during migration?
Which cost optimization tactics deliver results?
What comes after migration?
When does AWS to Azure migration make business sense?
Businesses typically consider migrating from AWS to Azure when their technology stack is deeply aligned with Microsoft products, especially if day‑to‑day operations rely on Windows Server, SQL Server, Active Directory, or Microsoft 365. Azure offers native integration within the Microsoft ecosystem, often providing operational efficiencies that can be challenging to replicate on AWS, even with additional third-party tools.
Migrating selected workloads from AWS to Azure can support a broader multi‑cloud strategy by diversifying provider risk while taking advantage of Azure’s strengths in analytics services (such as Synapse and Fabric) and hybrid cloud management with Azure Arc. Some pursue vendor independence as strategic insurance. Others want specific capabilities their AWS environment cannot provide regardless of configuration complexity.
Cost savings can be a reason to move from AWS to Azure, but only when the licensing model works in your favor. The strongest financial upside appears when existing Microsoft licenses with Software Assurance can be used with Azure Hybrid Benefit, while in other cases the cost difference between AWS and Azure may be small or even negligible.
Before deciding to migrate, ask yourself:
Will moving to Azure actually make our daily work easier?
What assessment steps are required before migration?
Start with a complete inventory of AWS resources. Document EC2 instances, RDS databases, S3 buckets, Lambda functions, and networking configurations. Azure Migrate provides discovery tools that scan your environment and generate detailed reports.
Collect specific data for each area using appropriate AWS tools:
Assessment Area | Data to Collect | Tools to Use |
Compute resources | Instance types, vCPUs, memory, storage | AWS Systems Manager, CloudWatch |
Database workloads | Engine versions, storage size, IOPS, backup frequency | RDS Performance Insights |
Network topology | VPC configuration, subnets, routing tables, bandwidth usage | VPC Flow Logs, CloudWatch |
Application dependencies | Service-to-service calls, API endpoints, batch jobs | AWS X-Ray, CloudTrail |
Map dependencies between applications and services. A payment system might connect to three databases, two APIs, and a message queue. Breaking these connections during migration causes downtime. Dependency mapping reveals which workloads must move together.
Analyze CloudWatch metrics for the past 90 days. CPU utilization, memory consumption, network traffic, and storage I/O patterns inform right-sizing decisions. An EC2 instance running at 15% CPU wastes money in both AWS and Azure.
Conduct a security audit. Your AWS security groups, IAM policies, and encryption settings need equivalents in the new platform. Both AWS and Azure offer a wide range of compliance certifications, but it is important to check that their controls match your specific regulatory needs.
Test network connectivity between remaining AWS resources and your new Azure environment. ExpressRoute provides dedicated circuits, while VPN gateways offer encrypted tunnels for lower-volume connections.
How much does AWS to Azure migration cost?
Migration costs break into planning, execution, and optimization. Planning includes assessment tools, consultations, and dependency mapping. For small migrations with 10–50 workloads, planning alone often lands in the tens of thousands of dollars, while large enterprise projects can reach a few hundred thousand dollars before any servers are moved.
Professional services cost $150 to $300 per hour. Some Azure assessment and migration tools are free to start with, while others are charged per protected instance or per server on a monthly basis, so pricing needs to be checked in the current Azure calculator.
Data egress from AWS creates expenses many companies underestimate. Moving 10TB costs approximately $920 in AWS fees, as an illustrative estimate. Actual costs vary by region, pricing tier, and discounts. Azure Data Box handles 40TB to 500TB offline for $300 to $500 plus shipping. ExpressRoute circuits add a fixed monthly cost that depends on bandwidth and region.
Staff training prevents expensive mistakes. Azure certifications cost $165 per exam with 40 to 80 hours study time required.
Post-migration cost reduction achieves 20 to 30% savings through reserved instances and right-sizing, based on typical industry scenarios rather than guaranteed results. ROI appears within 12 to 18 months if teams implement recommendations. For developing your cloud migration strategy, contact the Streamlogic team.
Which Azure tools simplify the migration process?
Microsoft provides specialized tools for each migration phase:
Tool | Primary Function | Key Benefit |
Azure Migrate | Discovery and assessment | Provides right-sizing recommendations and cost estimates |
Azure Site Recovery | VM replication and failover | Enables near-zero downtime migrations |
Azure Database Migration Service | Database schema and data transfer | Automates complex database conversions |
Azure Data Box | Offline data transfer | Moves petabytes without network bottlenecks |
Microsoft Azure Migrate provides the central hub for discovery, assessment, and tracking. It supports server, database, and web application migrations through one interface.
Azure Site Recovery handles replication and disaster recovery. It continuously syncs AWS workloads to the platform for near-zero-downtime migrations. Test failovers validate configurations without disrupting production.
Azure Database Migration Service moves data from AWS RDS to SQL Database, PostgreSQL, and MySQL with continuous sync to minimize downtime.
Azure Data Box accelerates transfers by shipping physical storage devices (40TB to 1PB) to your location. Load data locally and ship back for upload.
What migration strategy fits your workload?
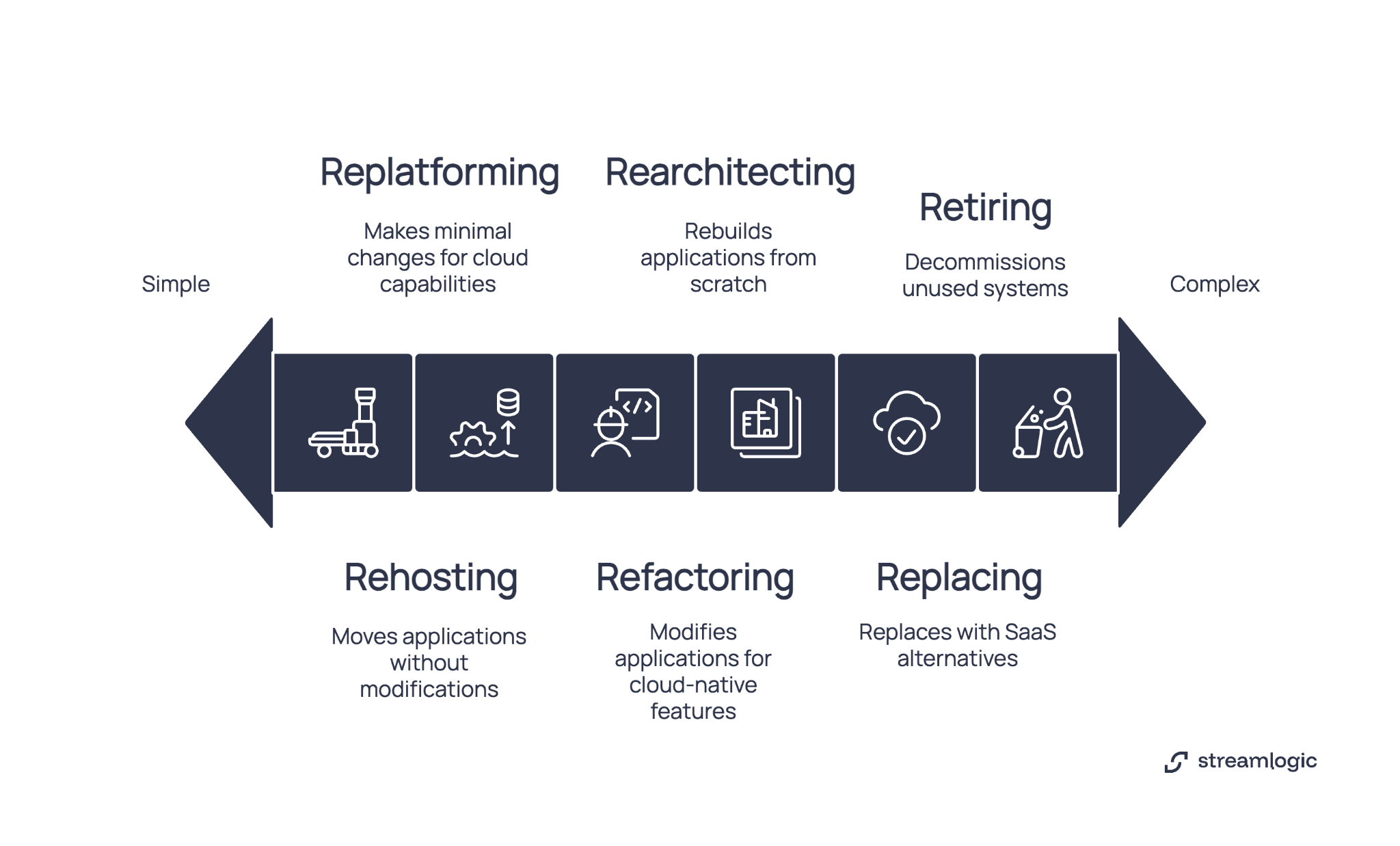
Rehosting (lift and shift) moves applications without modifications. Replicate AWS EC2 as VM with identical setup. Fastest approach but misses platform features.
Replatforming makes minimal changes for cloud capabilities. Migrating AWS RDS to Azure SQL Database keeps schemas but uses managed services. Balances speed with benefits.
Refactoring modifies applications for cloud-native features. Converting monoliths into microservices requires development effort but improves scalability.
Rearchitecting rebuilds applications from scratch when existing apps cannot meet requirements. Budget 6 to 12 months.
Replacing with SaaS alternatives eliminates infrastructure management. Migrating from self-hosted to managed services trades control for simplicity.
Retiring unused workloads reduces scope. Decommission systems nobody uses anymore.
How do you execute data transfer at scale?
Network bandwidth determines speed. As a rough estimate, a 100 Mbps link can move about 1 TB of data in around a day, assuming stable throughput and no major interruptions. Calculate AWS egress fees before starting because surprise bills damage budgets.
Azure Data Box serves projects moving 40TB or more. Load data locally at disk speed, ship devices for upload within 7 to 10 days. Costs $300 to $500 per device.
ExpressRoute provides a private, dedicated connection to Azure that bypasses the public internet, but it adds a recurring monthly fee that increases with bandwidth and region.
Incremental replication minimizes cutover downtime. Initial sync transfers all data while subsequent syncs only move changes. Azure Site Recovery handles this automatically for VMs.
Parallel transfers accelerate migration using multiple connections. Monitor utilization to avoid saturation. Most companies find 60 to 70% utilization optimal.
What security measures protect your migration?
Start with a security audit of AWS. Document IAM policies, security groups, and encryption settings. Map each AWS control to equivalent protections. Azure Active Directory replaces IAM while Network Security Groups replace security groups.
Map AWS security controls to Azure equivalents:
Security Layer | AWS Equivalent | Azure Implementation |
Network isolation | Security Groups | Network Security Groups (NSG) |
Identity and access | IAM | Azure Active Directory + RBAC |
Encryption at rest | EBS encryption | Azure Disk Encryption |
Key management | AWS KMS | Azure Key Vault |
Encrypt data in transit and at rest. Azure Storage Service Encryption handles data automatically. Require TLS 1.2 or higher for connections.
Implement identity and access management from day one. Configure role-based access control for least privilege. Multi-factor authentication should be mandatory for admin access.
Monitor traffic during and after migration. Network Watcher captures flow logs while Security Center assesses against best practices.
Test security controls before production. Conduct penetration testing and vulnerability scanning while rollback remains easy.
How can you minimize downtime during migration?
Continuous replication keeps Azure synchronized with AWS until cutover. Site Recovery replicates VMs and data in real time. Changes in AWS flow to the platform automatically. Stop source instances and redirect traffic with minimal delay.
DNS cutover provides fast transition. Update DNS records to Azure endpoints. Set low TTL values (5 to 15 minutes) before migration so changes propagate quickly.
Blue-green deployment runs both environments simultaneously. Keep AWS running while validating the new platform. Route test traffic to the new environment before full cutover.
Pilot migrations test procedures with non-critical workloads first. Start with development environments to refine processes before production. For teams needing additional expertise, staff augmentation with experienced cloud engineers can accelerate the migration process.
Maintenance windows schedule migrations during low-usage periods. Weekends or overnight slots minimize user impact. Have rollback plans ready.
Which cost optimization tactics deliver results?
Prioritize tactics based on savings potential and implementation effort:
Optimization Tactic | Potential Savings | Implementation Effort | Payback Period |
Azure Hybrid Benefit | 40-80% on Windows/SQL | Low (licensing only) | Immediate |
Reserved Instances | Up to 72% on compute | Low (purchasing decision) | Monthly from purchase |
Right-sizing VMs | 20-30% on compute | Medium (monitoring and adjustment) | 1-2 months |
Auto-scaling | 15-40% on variable workloads | High (architecture changes) | 3-6 months |
Azure Hybrid Benefit helps reduce cloud infrastructure costs with immediate savings for Windows Server or SQL Server licenses with Software Assurance. Businesses reduce compute costs by 40 to 80% compared to pay as you go. Apply benefits to VMs and SQL databases.
Reserved Instances cut costs up to 72% for continuous workloads. Commit to one or three year terms for specific VM sizes. Longer commitments provide larger discounts.
Azure Savings Plans offer 65% discounts with flexibility. Commit to fixed hourly amounts across computer services. Savings apply automatically to highest cost resources.
*These percentages are indicative ranges based on publicly available Microsoft guidance and common customer scenarios.
Right-sizing eliminates waste. VMs running at 15% CPU can drop to half size and cut costs in half. Advisor provides cost reduction recommendations.
Auto-scaling matches capacity to demand. Add instances when load increases and remove when traffic drops.
Storage tiering reduces costs for infrequent data. Hot tier costs $0.0184 per GB monthly while archive tier costs $0.00099 per GB.
What comes after migration?
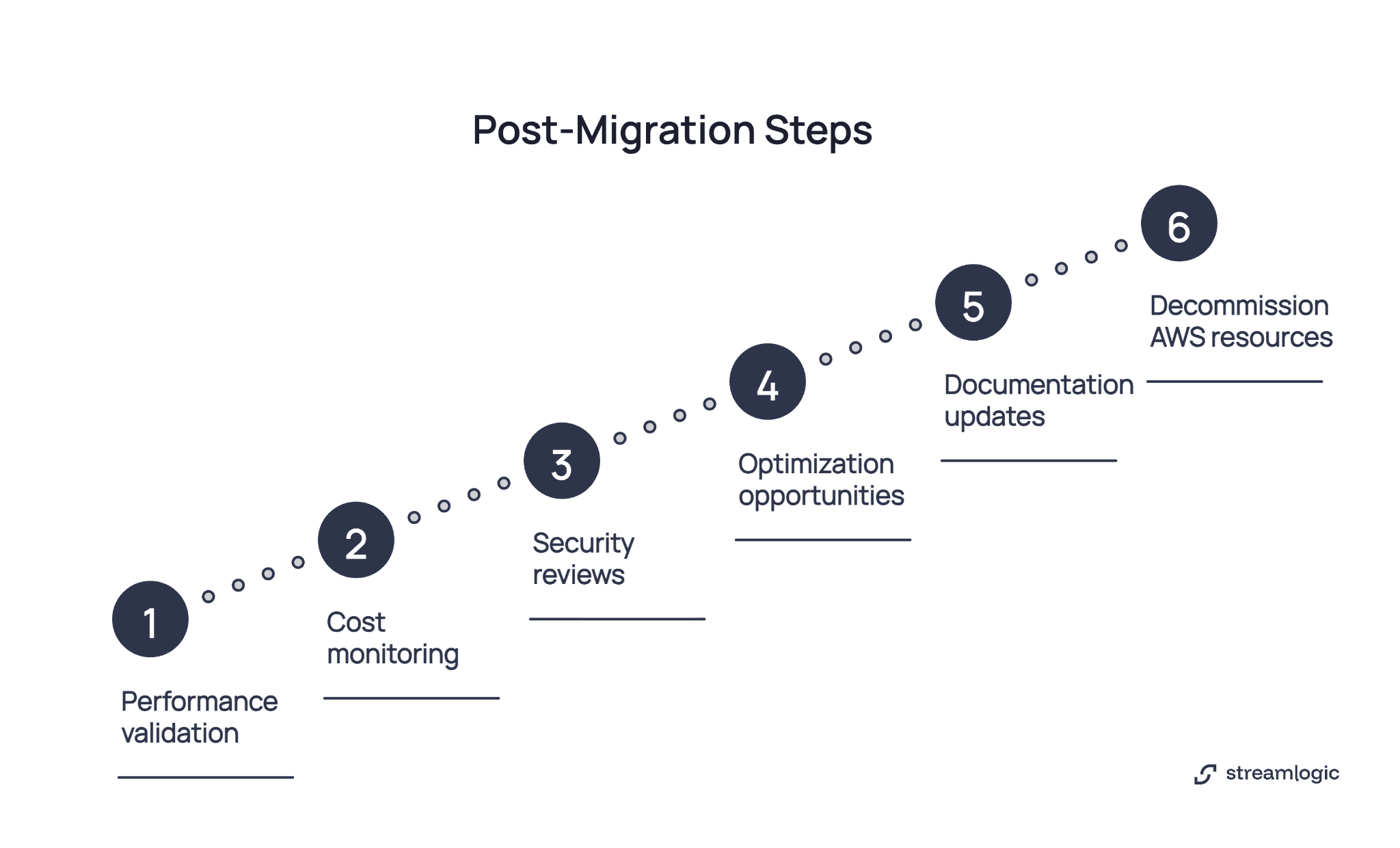
Performance validation confirms applications run as expected in your new environment. Test response times against AWS baselines while monitoring throughput under realistic load conditions. Error rates should match or improve compared to previous performance metrics. Address any degradation immediately because users won't tolerate slow applications regardless of which cloud provider hosts them.
Cost monitoring prevents budget surprises that damage executive confidence in cloud initiatives. Enable Cost Management and set budget alerts before spending exceeds projections. Review spending daily during the first month, then weekly for the next quarter. Unexpected costs often come from data transfer between regions, storage tier misconfiguration, or test resources left running after engineers finish their work.
Security reviews ensure controls survived migration intact. Run vulnerability scans and validate compliance settings that match your industry requirements. The Security Center provides continuous assessment against best practices. Address high-severity findings within 24 hours before they create exploitable gaps.
Optimization opportunities emerge after applications run for several weeks. Advisor generates recommendations for cost, performance, and security improvements based on actual usage patterns. Implement high-impact recommendations first instead of trying to address every minor suggestion.
Documentation updates capture platform-specific procedures your team needs for daily operations. Update runbooks, disaster recovery plans, and operational procedures with new tool names and processes. Train teams on monitoring and troubleshooting workflows because knowledge gaps create risk when incidents occur.
Decommission AWS resources only after validating platform stability for at least 30-90 days. This provides insurance against unexpected issues that appear only under production load. Once confident in operations, terminate AWS resources methodically while downloading final backups before destroying storage volumes.
FAQs
What are the main challenges of AWS to Azure migration?
AWS and Azure implement services differently, so direct translation rarely works and applications often need reconfiguration or redesign. Data transfer takes time and risks downtime, while security settings require manual remapping since compliance certifications differ between platforms. Applications built for AWS-specific services need code modifications, and dependencies create unexpected complexity during migration. The solution is to assess thoroughly before migrating, test everything in Azure first, and use replication tools to minimize downtime.
Can you migrate without downtime?
For some workloads, Azure Site Recovery and similar tools can keep data in sync so that the final cutover only takes minutes, but in practice there is usually at least a short maintenance window.
How long does data transfer take?
A 100Mbps connection moves 1TB in 24 hours. Azure Data Box handles 40TB+ transfers offline within 7-10 days.
Do security configurations transfer automatically?
No. AWS security groups and IAM policies require manual mapping to Azure Active Directory and Network Security Groups.
What about AWS costs during migration?
You pay for both platforms during migration. Keep AWS running 30-90 days post-cutover for rollback insurance.
Which certification should teams get first?
Azure Administrator (AZ-104) for operations teams. Solutions Architect Expert (AZ-305) for architects. $165 per exam.
Conclusion
Migrate to Azure when you need tight Microsoft integration. The business case requires three factors: existing Microsoft licenses with Software Assurance, workloads running Windows Server or SQL Server, and operations dependent on Microsoft tooling.
Assessment determines success. Companies that map dependencies, collect performance metrics, and test security controls before migration avoid expensive mistakes. Those that skip planning face extended downtime, cost overruns, and security gaps.
Don't migrate if: You run primarily Linux workloads without Microsoft dependencies, lack existing Microsoft licenses, or cannot justify 4-6 months of planning and execution time. AWS serves those scenarios equally well.
Do migrate if: Your stack revolves around Microsoft products, you hold Windows Server or SQL Server licenses with Software Assurance, or multi-cloud strategy requires distributing workloads across providers.
For expert guidance on your cloud migration consulting needs, book a session with our Cloud Experts.

Denis Avramenko
CTO, Co-Founder, Streamlogic


Technology Articles
Cloud Modernization Strategy Guide for Enterprises 2026
Dec 18, 2025


Technology Articles
How to Develop Cloud Applications: Complete Planning to Deployment Roadmap 2026
Dec 18, 2025


Technology Articles
Cloud Compliance in 2026: Navigating Standards, Strategies, and Best Practices
Dec 12, 2025


Technology Articles
Cloud Modernization Strategy Guide for Enterprises 2026
Dec 18, 2025


Technology Articles
How to Develop Cloud Applications: Complete Planning to Deployment Roadmap 2026
Dec 18, 2025


Technology Articles
Cloud Compliance in 2026: Navigating Standards, Strategies, and Best Practices
Dec 12, 2025
Reading time: 8 minutes
Table of Contents
When does AWS to Azure migration make business sense?
What assessment steps are required before migration?
How much does AWS to Azure migration cost?
Which Azure tools simplify the migration process?
What migration strategy fits your workload?
How do you execute data transfer at scale?
What security measures protect your migration?
How can you minimize downtime during migration?
Which cost optimization tactics deliver results?
What comes after migration?
When does AWS to Azure migration make business sense?
Businesses typically consider migrating from AWS to Azure when their technology stack is deeply aligned with Microsoft products, especially if day‑to‑day operations rely on Windows Server, SQL Server, Active Directory, or Microsoft 365. Azure offers native integration within the Microsoft ecosystem, often providing operational efficiencies that can be challenging to replicate on AWS, even with additional third-party tools.
Migrating selected workloads from AWS to Azure can support a broader multi‑cloud strategy by diversifying provider risk while taking advantage of Azure’s strengths in analytics services (such as Synapse and Fabric) and hybrid cloud management with Azure Arc. Some pursue vendor independence as strategic insurance. Others want specific capabilities their AWS environment cannot provide regardless of configuration complexity.
Cost savings can be a reason to move from AWS to Azure, but only when the licensing model works in your favor. The strongest financial upside appears when existing Microsoft licenses with Software Assurance can be used with Azure Hybrid Benefit, while in other cases the cost difference between AWS and Azure may be small or even negligible.
Before deciding to migrate, ask yourself:
Will moving to Azure actually make our daily work easier?
What assessment steps are required before migration?
Start with a complete inventory of AWS resources. Document EC2 instances, RDS databases, S3 buckets, Lambda functions, and networking configurations. Azure Migrate provides discovery tools that scan your environment and generate detailed reports.
Collect specific data for each area using appropriate AWS tools:
Assessment Area | Data to Collect | Tools to Use |
Compute resources | Instance types, vCPUs, memory, storage | AWS Systems Manager, CloudWatch |
Database workloads | Engine versions, storage size, IOPS, backup frequency | RDS Performance Insights |
Network topology | VPC configuration, subnets, routing tables, bandwidth usage | VPC Flow Logs, CloudWatch |
Application dependencies | Service-to-service calls, API endpoints, batch jobs | AWS X-Ray, CloudTrail |
Map dependencies between applications and services. A payment system might connect to three databases, two APIs, and a message queue. Breaking these connections during migration causes downtime. Dependency mapping reveals which workloads must move together.
Analyze CloudWatch metrics for the past 90 days. CPU utilization, memory consumption, network traffic, and storage I/O patterns inform right-sizing decisions. An EC2 instance running at 15% CPU wastes money in both AWS and Azure.
Conduct a security audit. Your AWS security groups, IAM policies, and encryption settings need equivalents in the new platform. Both AWS and Azure offer a wide range of compliance certifications, but it is important to check that their controls match your specific regulatory needs.
Test network connectivity between remaining AWS resources and your new Azure environment. ExpressRoute provides dedicated circuits, while VPN gateways offer encrypted tunnels for lower-volume connections.
How much does AWS to Azure migration cost?
Migration costs break into planning, execution, and optimization. Planning includes assessment tools, consultations, and dependency mapping. For small migrations with 10–50 workloads, planning alone often lands in the tens of thousands of dollars, while large enterprise projects can reach a few hundred thousand dollars before any servers are moved.
Professional services cost $150 to $300 per hour. Some Azure assessment and migration tools are free to start with, while others are charged per protected instance or per server on a monthly basis, so pricing needs to be checked in the current Azure calculator.
Data egress from AWS creates expenses many companies underestimate. Moving 10TB costs approximately $920 in AWS fees, as an illustrative estimate. Actual costs vary by region, pricing tier, and discounts. Azure Data Box handles 40TB to 500TB offline for $300 to $500 plus shipping. ExpressRoute circuits add a fixed monthly cost that depends on bandwidth and region.
Staff training prevents expensive mistakes. Azure certifications cost $165 per exam with 40 to 80 hours study time required.
Post-migration cost reduction achieves 20 to 30% savings through reserved instances and right-sizing, based on typical industry scenarios rather than guaranteed results. ROI appears within 12 to 18 months if teams implement recommendations. For developing your cloud migration strategy, contact the Streamlogic team.
Which Azure tools simplify the migration process?
Microsoft provides specialized tools for each migration phase:
Tool | Primary Function | Key Benefit |
Azure Migrate | Discovery and assessment | Provides right-sizing recommendations and cost estimates |
Azure Site Recovery | VM replication and failover | Enables near-zero downtime migrations |
Azure Database Migration Service | Database schema and data transfer | Automates complex database conversions |
Azure Data Box | Offline data transfer | Moves petabytes without network bottlenecks |
Microsoft Azure Migrate provides the central hub for discovery, assessment, and tracking. It supports server, database, and web application migrations through one interface.
Azure Site Recovery handles replication and disaster recovery. It continuously syncs AWS workloads to the platform for near-zero-downtime migrations. Test failovers validate configurations without disrupting production.
Azure Database Migration Service moves data from AWS RDS to SQL Database, PostgreSQL, and MySQL with continuous sync to minimize downtime.
Azure Data Box accelerates transfers by shipping physical storage devices (40TB to 1PB) to your location. Load data locally and ship back for upload.
What migration strategy fits your workload?

Rehosting (lift and shift) moves applications without modifications. Replicate AWS EC2 as VM with identical setup. Fastest approach but misses platform features.
Replatforming makes minimal changes for cloud capabilities. Migrating AWS RDS to Azure SQL Database keeps schemas but uses managed services. Balances speed with benefits.
Refactoring modifies applications for cloud-native features. Converting monoliths into microservices requires development effort but improves scalability.
Rearchitecting rebuilds applications from scratch when existing apps cannot meet requirements. Budget 6 to 12 months.
Replacing with SaaS alternatives eliminates infrastructure management. Migrating from self-hosted to managed services trades control for simplicity.
Retiring unused workloads reduces scope. Decommission systems nobody uses anymore.
How do you execute data transfer at scale?
Network bandwidth determines speed. As a rough estimate, a 100 Mbps link can move about 1 TB of data in around a day, assuming stable throughput and no major interruptions. Calculate AWS egress fees before starting because surprise bills damage budgets.
Azure Data Box serves projects moving 40TB or more. Load data locally at disk speed, ship devices for upload within 7 to 10 days. Costs $300 to $500 per device.
ExpressRoute provides a private, dedicated connection to Azure that bypasses the public internet, but it adds a recurring monthly fee that increases with bandwidth and region.
Incremental replication minimizes cutover downtime. Initial sync transfers all data while subsequent syncs only move changes. Azure Site Recovery handles this automatically for VMs.
Parallel transfers accelerate migration using multiple connections. Monitor utilization to avoid saturation. Most companies find 60 to 70% utilization optimal.
What security measures protect your migration?
Start with a security audit of AWS. Document IAM policies, security groups, and encryption settings. Map each AWS control to equivalent protections. Azure Active Directory replaces IAM while Network Security Groups replace security groups.
Map AWS security controls to Azure equivalents:
Security Layer | AWS Equivalent | Azure Implementation |
Network isolation | Security Groups | Network Security Groups (NSG) |
Identity and access | IAM | Azure Active Directory + RBAC |
Encryption at rest | EBS encryption | Azure Disk Encryption |
Key management | AWS KMS | Azure Key Vault |
Encrypt data in transit and at rest. Azure Storage Service Encryption handles data automatically. Require TLS 1.2 or higher for connections.
Implement identity and access management from day one. Configure role-based access control for least privilege. Multi-factor authentication should be mandatory for admin access.
Monitor traffic during and after migration. Network Watcher captures flow logs while Security Center assesses against best practices.
Test security controls before production. Conduct penetration testing and vulnerability scanning while rollback remains easy.
How can you minimize downtime during migration?
Continuous replication keeps Azure synchronized with AWS until cutover. Site Recovery replicates VMs and data in real time. Changes in AWS flow to the platform automatically. Stop source instances and redirect traffic with minimal delay.
DNS cutover provides fast transition. Update DNS records to Azure endpoints. Set low TTL values (5 to 15 minutes) before migration so changes propagate quickly.
Blue-green deployment runs both environments simultaneously. Keep AWS running while validating the new platform. Route test traffic to the new environment before full cutover.
Pilot migrations test procedures with non-critical workloads first. Start with development environments to refine processes before production. For teams needing additional expertise, staff augmentation with experienced cloud engineers can accelerate the migration process.
Maintenance windows schedule migrations during low-usage periods. Weekends or overnight slots minimize user impact. Have rollback plans ready.
Which cost optimization tactics deliver results?
Prioritize tactics based on savings potential and implementation effort:
Optimization Tactic | Potential Savings | Implementation Effort | Payback Period |
Azure Hybrid Benefit | 40-80% on Windows/SQL | Low (licensing only) | Immediate |
Reserved Instances | Up to 72% on compute | Low (purchasing decision) | Monthly from purchase |
Right-sizing VMs | 20-30% on compute | Medium (monitoring and adjustment) | 1-2 months |
Auto-scaling | 15-40% on variable workloads | High (architecture changes) | 3-6 months |
Azure Hybrid Benefit helps reduce cloud infrastructure costs with immediate savings for Windows Server or SQL Server licenses with Software Assurance. Businesses reduce compute costs by 40 to 80% compared to pay as you go. Apply benefits to VMs and SQL databases.
Reserved Instances cut costs up to 72% for continuous workloads. Commit to one or three year terms for specific VM sizes. Longer commitments provide larger discounts.
Azure Savings Plans offer 65% discounts with flexibility. Commit to fixed hourly amounts across computer services. Savings apply automatically to highest cost resources.
*These percentages are indicative ranges based on publicly available Microsoft guidance and common customer scenarios.
Right-sizing eliminates waste. VMs running at 15% CPU can drop to half size and cut costs in half. Advisor provides cost reduction recommendations.
Auto-scaling matches capacity to demand. Add instances when load increases and remove when traffic drops.
Storage tiering reduces costs for infrequent data. Hot tier costs $0.0184 per GB monthly while archive tier costs $0.00099 per GB.
What comes after migration?

Performance validation confirms applications run as expected in your new environment. Test response times against AWS baselines while monitoring throughput under realistic load conditions. Error rates should match or improve compared to previous performance metrics. Address any degradation immediately because users won't tolerate slow applications regardless of which cloud provider hosts them.
Cost monitoring prevents budget surprises that damage executive confidence in cloud initiatives. Enable Cost Management and set budget alerts before spending exceeds projections. Review spending daily during the first month, then weekly for the next quarter. Unexpected costs often come from data transfer between regions, storage tier misconfiguration, or test resources left running after engineers finish their work.
Security reviews ensure controls survived migration intact. Run vulnerability scans and validate compliance settings that match your industry requirements. The Security Center provides continuous assessment against best practices. Address high-severity findings within 24 hours before they create exploitable gaps.
Optimization opportunities emerge after applications run for several weeks. Advisor generates recommendations for cost, performance, and security improvements based on actual usage patterns. Implement high-impact recommendations first instead of trying to address every minor suggestion.
Documentation updates capture platform-specific procedures your team needs for daily operations. Update runbooks, disaster recovery plans, and operational procedures with new tool names and processes. Train teams on monitoring and troubleshooting workflows because knowledge gaps create risk when incidents occur.
Decommission AWS resources only after validating platform stability for at least 30-90 days. This provides insurance against unexpected issues that appear only under production load. Once confident in operations, terminate AWS resources methodically while downloading final backups before destroying storage volumes.
FAQs
What are the main challenges of AWS to Azure migration?
AWS and Azure implement services differently, so direct translation rarely works and applications often need reconfiguration or redesign. Data transfer takes time and risks downtime, while security settings require manual remapping since compliance certifications differ between platforms. Applications built for AWS-specific services need code modifications, and dependencies create unexpected complexity during migration. The solution is to assess thoroughly before migrating, test everything in Azure first, and use replication tools to minimize downtime.
Can you migrate without downtime?
For some workloads, Azure Site Recovery and similar tools can keep data in sync so that the final cutover only takes minutes, but in practice there is usually at least a short maintenance window.
How long does data transfer take?
A 100Mbps connection moves 1TB in 24 hours. Azure Data Box handles 40TB+ transfers offline within 7-10 days.
Do security configurations transfer automatically?
No. AWS security groups and IAM policies require manual mapping to Azure Active Directory and Network Security Groups.
What about AWS costs during migration?
You pay for both platforms during migration. Keep AWS running 30-90 days post-cutover for rollback insurance.
Which certification should teams get first?
Azure Administrator (AZ-104) for operations teams. Solutions Architect Expert (AZ-305) for architects. $165 per exam.
Conclusion
Migrate to Azure when you need tight Microsoft integration. The business case requires three factors: existing Microsoft licenses with Software Assurance, workloads running Windows Server or SQL Server, and operations dependent on Microsoft tooling.
Assessment determines success. Companies that map dependencies, collect performance metrics, and test security controls before migration avoid expensive mistakes. Those that skip planning face extended downtime, cost overruns, and security gaps.
Don't migrate if: You run primarily Linux workloads without Microsoft dependencies, lack existing Microsoft licenses, or cannot justify 4-6 months of planning and execution time. AWS serves those scenarios equally well.
Do migrate if: Your stack revolves around Microsoft products, you hold Windows Server or SQL Server licenses with Software Assurance, or multi-cloud strategy requires distributing workloads across providers.
For expert guidance on your cloud migration consulting needs, book a session with our Cloud Experts.

Denis Avramenko
CTO, Co-Founder, Streamlogic
Reading time: 8 minutes
Table of Contents
When does AWS to Azure migration make business sense?
What assessment steps are required before migration?
How much does AWS to Azure migration cost?
Which Azure tools simplify the migration process?
What migration strategy fits your workload?
How do you execute data transfer at scale?
What security measures protect your migration?
How can you minimize downtime during migration?
Which cost optimization tactics deliver results?
What comes after migration?
When does AWS to Azure migration make business sense?
Businesses typically consider migrating from AWS to Azure when their technology stack is deeply aligned with Microsoft products, especially if day‑to‑day operations rely on Windows Server, SQL Server, Active Directory, or Microsoft 365. Azure offers native integration within the Microsoft ecosystem, often providing operational efficiencies that can be challenging to replicate on AWS, even with additional third-party tools.
Migrating selected workloads from AWS to Azure can support a broader multi‑cloud strategy by diversifying provider risk while taking advantage of Azure’s strengths in analytics services (such as Synapse and Fabric) and hybrid cloud management with Azure Arc. Some pursue vendor independence as strategic insurance. Others want specific capabilities their AWS environment cannot provide regardless of configuration complexity.
Cost savings can be a reason to move from AWS to Azure, but only when the licensing model works in your favor. The strongest financial upside appears when existing Microsoft licenses with Software Assurance can be used with Azure Hybrid Benefit, while in other cases the cost difference between AWS and Azure may be small or even negligible.
Before deciding to migrate, ask yourself:
Will moving to Azure actually make our daily work easier?
What assessment steps are required before migration?
Start with a complete inventory of AWS resources. Document EC2 instances, RDS databases, S3 buckets, Lambda functions, and networking configurations. Azure Migrate provides discovery tools that scan your environment and generate detailed reports.
Collect specific data for each area using appropriate AWS tools:
Assessment Area | Data to Collect | Tools to Use |
Compute resources | Instance types, vCPUs, memory, storage | AWS Systems Manager, CloudWatch |
Database workloads | Engine versions, storage size, IOPS, backup frequency | RDS Performance Insights |
Network topology | VPC configuration, subnets, routing tables, bandwidth usage | VPC Flow Logs, CloudWatch |
Application dependencies | Service-to-service calls, API endpoints, batch jobs | AWS X-Ray, CloudTrail |
Map dependencies between applications and services. A payment system might connect to three databases, two APIs, and a message queue. Breaking these connections during migration causes downtime. Dependency mapping reveals which workloads must move together.
Analyze CloudWatch metrics for the past 90 days. CPU utilization, memory consumption, network traffic, and storage I/O patterns inform right-sizing decisions. An EC2 instance running at 15% CPU wastes money in both AWS and Azure.
Conduct a security audit. Your AWS security groups, IAM policies, and encryption settings need equivalents in the new platform. Both AWS and Azure offer a wide range of compliance certifications, but it is important to check that their controls match your specific regulatory needs.
Test network connectivity between remaining AWS resources and your new Azure environment. ExpressRoute provides dedicated circuits, while VPN gateways offer encrypted tunnels for lower-volume connections.
How much does AWS to Azure migration cost?
Migration costs break into planning, execution, and optimization. Planning includes assessment tools, consultations, and dependency mapping. For small migrations with 10–50 workloads, planning alone often lands in the tens of thousands of dollars, while large enterprise projects can reach a few hundred thousand dollars before any servers are moved.
Professional services cost $150 to $300 per hour. Some Azure assessment and migration tools are free to start with, while others are charged per protected instance or per server on a monthly basis, so pricing needs to be checked in the current Azure calculator.
Data egress from AWS creates expenses many companies underestimate. Moving 10TB costs approximately $920 in AWS fees, as an illustrative estimate. Actual costs vary by region, pricing tier, and discounts. Azure Data Box handles 40TB to 500TB offline for $300 to $500 plus shipping. ExpressRoute circuits add a fixed monthly cost that depends on bandwidth and region.
Staff training prevents expensive mistakes. Azure certifications cost $165 per exam with 40 to 80 hours study time required.
Post-migration cost reduction achieves 20 to 30% savings through reserved instances and right-sizing, based on typical industry scenarios rather than guaranteed results. ROI appears within 12 to 18 months if teams implement recommendations. For developing your cloud migration strategy, contact the Streamlogic team.
Which Azure tools simplify the migration process?
Microsoft provides specialized tools for each migration phase:
Tool | Primary Function | Key Benefit |
Azure Migrate | Discovery and assessment | Provides right-sizing recommendations and cost estimates |
Azure Site Recovery | VM replication and failover | Enables near-zero downtime migrations |
Azure Database Migration Service | Database schema and data transfer | Automates complex database conversions |
Azure Data Box | Offline data transfer | Moves petabytes without network bottlenecks |
Microsoft Azure Migrate provides the central hub for discovery, assessment, and tracking. It supports server, database, and web application migrations through one interface.
Azure Site Recovery handles replication and disaster recovery. It continuously syncs AWS workloads to the platform for near-zero-downtime migrations. Test failovers validate configurations without disrupting production.
Azure Database Migration Service moves data from AWS RDS to SQL Database, PostgreSQL, and MySQL with continuous sync to minimize downtime.
Azure Data Box accelerates transfers by shipping physical storage devices (40TB to 1PB) to your location. Load data locally and ship back for upload.
What migration strategy fits your workload?

Rehosting (lift and shift) moves applications without modifications. Replicate AWS EC2 as VM with identical setup. Fastest approach but misses platform features.
Replatforming makes minimal changes for cloud capabilities. Migrating AWS RDS to Azure SQL Database keeps schemas but uses managed services. Balances speed with benefits.
Refactoring modifies applications for cloud-native features. Converting monoliths into microservices requires development effort but improves scalability.
Rearchitecting rebuilds applications from scratch when existing apps cannot meet requirements. Budget 6 to 12 months.
Replacing with SaaS alternatives eliminates infrastructure management. Migrating from self-hosted to managed services trades control for simplicity.
Retiring unused workloads reduces scope. Decommission systems nobody uses anymore.
How do you execute data transfer at scale?
Network bandwidth determines speed. As a rough estimate, a 100 Mbps link can move about 1 TB of data in around a day, assuming stable throughput and no major interruptions. Calculate AWS egress fees before starting because surprise bills damage budgets.
Azure Data Box serves projects moving 40TB or more. Load data locally at disk speed, ship devices for upload within 7 to 10 days. Costs $300 to $500 per device.
ExpressRoute provides a private, dedicated connection to Azure that bypasses the public internet, but it adds a recurring monthly fee that increases with bandwidth and region.
Incremental replication minimizes cutover downtime. Initial sync transfers all data while subsequent syncs only move changes. Azure Site Recovery handles this automatically for VMs.
Parallel transfers accelerate migration using multiple connections. Monitor utilization to avoid saturation. Most companies find 60 to 70% utilization optimal.
What security measures protect your migration?
Start with a security audit of AWS. Document IAM policies, security groups, and encryption settings. Map each AWS control to equivalent protections. Azure Active Directory replaces IAM while Network Security Groups replace security groups.
Map AWS security controls to Azure equivalents:
Security Layer | AWS Equivalent | Azure Implementation |
Network isolation | Security Groups | Network Security Groups (NSG) |
Identity and access | IAM | Azure Active Directory + RBAC |
Encryption at rest | EBS encryption | Azure Disk Encryption |
Key management | AWS KMS | Azure Key Vault |
Encrypt data in transit and at rest. Azure Storage Service Encryption handles data automatically. Require TLS 1.2 or higher for connections.
Implement identity and access management from day one. Configure role-based access control for least privilege. Multi-factor authentication should be mandatory for admin access.
Monitor traffic during and after migration. Network Watcher captures flow logs while Security Center assesses against best practices.
Test security controls before production. Conduct penetration testing and vulnerability scanning while rollback remains easy.
How can you minimize downtime during migration?
Continuous replication keeps Azure synchronized with AWS until cutover. Site Recovery replicates VMs and data in real time. Changes in AWS flow to the platform automatically. Stop source instances and redirect traffic with minimal delay.
DNS cutover provides fast transition. Update DNS records to Azure endpoints. Set low TTL values (5 to 15 minutes) before migration so changes propagate quickly.
Blue-green deployment runs both environments simultaneously. Keep AWS running while validating the new platform. Route test traffic to the new environment before full cutover.
Pilot migrations test procedures with non-critical workloads first. Start with development environments to refine processes before production. For teams needing additional expertise, staff augmentation with experienced cloud engineers can accelerate the migration process.
Maintenance windows schedule migrations during low-usage periods. Weekends or overnight slots minimize user impact. Have rollback plans ready.
Which cost optimization tactics deliver results?
Prioritize tactics based on savings potential and implementation effort:
Optimization Tactic | Potential Savings | Implementation Effort | Payback Period |
Azure Hybrid Benefit | 40-80% on Windows/SQL | Low (licensing only) | Immediate |
Reserved Instances | Up to 72% on compute | Low (purchasing decision) | Monthly from purchase |
Right-sizing VMs | 20-30% on compute | Medium (monitoring and adjustment) | 1-2 months |
Auto-scaling | 15-40% on variable workloads | High (architecture changes) | 3-6 months |
Azure Hybrid Benefit helps reduce cloud infrastructure costs with immediate savings for Windows Server or SQL Server licenses with Software Assurance. Businesses reduce compute costs by 40 to 80% compared to pay as you go. Apply benefits to VMs and SQL databases.
Reserved Instances cut costs up to 72% for continuous workloads. Commit to one or three year terms for specific VM sizes. Longer commitments provide larger discounts.
Azure Savings Plans offer 65% discounts with flexibility. Commit to fixed hourly amounts across computer services. Savings apply automatically to highest cost resources.
*These percentages are indicative ranges based on publicly available Microsoft guidance and common customer scenarios.
Right-sizing eliminates waste. VMs running at 15% CPU can drop to half size and cut costs in half. Advisor provides cost reduction recommendations.
Auto-scaling matches capacity to demand. Add instances when load increases and remove when traffic drops.
Storage tiering reduces costs for infrequent data. Hot tier costs $0.0184 per GB monthly while archive tier costs $0.00099 per GB.
What comes after migration?

Performance validation confirms applications run as expected in your new environment. Test response times against AWS baselines while monitoring throughput under realistic load conditions. Error rates should match or improve compared to previous performance metrics. Address any degradation immediately because users won't tolerate slow applications regardless of which cloud provider hosts them.
Cost monitoring prevents budget surprises that damage executive confidence in cloud initiatives. Enable Cost Management and set budget alerts before spending exceeds projections. Review spending daily during the first month, then weekly for the next quarter. Unexpected costs often come from data transfer between regions, storage tier misconfiguration, or test resources left running after engineers finish their work.
Security reviews ensure controls survived migration intact. Run vulnerability scans and validate compliance settings that match your industry requirements. The Security Center provides continuous assessment against best practices. Address high-severity findings within 24 hours before they create exploitable gaps.
Optimization opportunities emerge after applications run for several weeks. Advisor generates recommendations for cost, performance, and security improvements based on actual usage patterns. Implement high-impact recommendations first instead of trying to address every minor suggestion.
Documentation updates capture platform-specific procedures your team needs for daily operations. Update runbooks, disaster recovery plans, and operational procedures with new tool names and processes. Train teams on monitoring and troubleshooting workflows because knowledge gaps create risk when incidents occur.
Decommission AWS resources only after validating platform stability for at least 30-90 days. This provides insurance against unexpected issues that appear only under production load. Once confident in operations, terminate AWS resources methodically while downloading final backups before destroying storage volumes.
FAQs
What are the main challenges of AWS to Azure migration?
AWS and Azure implement services differently, so direct translation rarely works and applications often need reconfiguration or redesign. Data transfer takes time and risks downtime, while security settings require manual remapping since compliance certifications differ between platforms. Applications built for AWS-specific services need code modifications, and dependencies create unexpected complexity during migration. The solution is to assess thoroughly before migrating, test everything in Azure first, and use replication tools to minimize downtime.
Can you migrate without downtime?
For some workloads, Azure Site Recovery and similar tools can keep data in sync so that the final cutover only takes minutes, but in practice there is usually at least a short maintenance window.
How long does data transfer take?
A 100Mbps connection moves 1TB in 24 hours. Azure Data Box handles 40TB+ transfers offline within 7-10 days.
Do security configurations transfer automatically?
No. AWS security groups and IAM policies require manual mapping to Azure Active Directory and Network Security Groups.
What about AWS costs during migration?
You pay for both platforms during migration. Keep AWS running 30-90 days post-cutover for rollback insurance.
Which certification should teams get first?
Azure Administrator (AZ-104) for operations teams. Solutions Architect Expert (AZ-305) for architects. $165 per exam.
Conclusion
Migrate to Azure when you need tight Microsoft integration. The business case requires three factors: existing Microsoft licenses with Software Assurance, workloads running Windows Server or SQL Server, and operations dependent on Microsoft tooling.
Assessment determines success. Companies that map dependencies, collect performance metrics, and test security controls before migration avoid expensive mistakes. Those that skip planning face extended downtime, cost overruns, and security gaps.
Don't migrate if: You run primarily Linux workloads without Microsoft dependencies, lack existing Microsoft licenses, or cannot justify 4-6 months of planning and execution time. AWS serves those scenarios equally well.
Do migrate if: Your stack revolves around Microsoft products, you hold Windows Server or SQL Server licenses with Software Assurance, or multi-cloud strategy requires distributing workloads across providers.
For expert guidance on your cloud migration consulting needs, book a session with our Cloud Experts.

Denis Avramenko
CTO, Co-Founder, Streamlogic


Technology Articles
Cloud Modernization Strategy Guide for Enterprises 2026
Dec 18, 2025


Technology Articles
How to Develop Cloud Applications: Complete Planning to Deployment Roadmap 2026
Dec 18, 2025


Technology Articles
Cloud Compliance in 2026: Navigating Standards, Strategies, and Best Practices
Dec 12, 2025
Tech Council
Technology Articles
How to Plan Your AWS to Azure Migration in 2026
Learn how to migrate from AWS to Azure with proven strategies, cost estimates, and Microsoft tools. A complete guide for cloud transitions in 2026.

Denis Avramenko
CTO, Co-Founder, Streamlogic
Dec 11, 2025

